Duplicate Content and SEO: Is It Bad for Rankings?
Mar 13, 2023
Table of Contents
What is duplicate content?
Causes of duplicate content
Copied content
HTTPS vs HTTP
URL variations
Session IDs
Thin content
Generic eCommerce product pages
Does duplicate content hurt your SEO?
Duplicate content penalty: fact or fiction?
How to avoid duplicate content SEO issues
Conclusion
Duplicate content can be a major obstacle for businesses and websites trying to maintain excellent SEO rankings.
Duplicate content can occur from having two or more web pages, posts, or URLs that have the same information and content. Having duplicate content on your website can lead to confusing search engine indexing, resulting in lower page visibility, fewer page views, and ultimately decreased conversions.
In this article, we will explore what duplicate content is, its causes, whether it hurts your SEO ranking, possible penalties, and how to fix it.
What is Duplicate Content Exactly?
Duplicate content, as defined by Google, is “substantive blocks of content within or across domains that either completely matches other content or are appreciably similar.”
Image source: Explore Insiders
In simpler terms, duplicate content occurs when there are multiple web pages that contain the same text, images, videos, titles, or meta descriptions.
Examples of duplicate content can include:
- Two web pages on the same website with the exact same title and description
- A webpage with two different URLs but identical contents
- Copied text from a published article on another domain
Causes of Duplicate Content
Duplicate content can be caused by a number of factors, the most common being copied content, HTTPS vs HTTP, and URL variations and structures. Below are explanations for each of these causes and how they can lead to duplicate content.
Copied Content
Copied content is the most common cause of duplicate content. This occurs when web pages contain text or other material that has been taken from another source without permission or attribution. Not only does this create duplicate versions of the same webpage on different websites, but it can lead to Search Engine Optimization (SEO) issues when it comes to ranking in search results.
This can also be a problem when you're syndicating some of your website's content to other publishers. If the publisher is not properly attributing the content back to you, it could cause duplicate content issues.
HTTPS vs HTTP
Image source: HTTPS.in
Another common cause for duplicate content is having the same website available in both HTTPS and HTTP formats. This means that the same website appears twice in search engine crawl results - once with an “https” prefix and again with an “http” prefix - which leads to identical versions of the website appearing in search engine results.
URL Variations and Structures
URL variations and structures also contribute to duplicate content issues. Much like having a website available on both HTTPS and HTTP formats, having two different URLs pointing to the same page can cause this issue as well.
For example, if your website's homepage is available at www.example-domain/ as well as www.example-domain/home/, then Google will see these two URLs as separate web pages with identical content, creating duplicate versions of your site in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Additionally, using various parameters such as filtering criteria (for example: ?sort=date) within a URL can also lead to multiple URLs pointing to a single page, causing similar issues with SERP listings.
Session IDs
Session IDs are unique identifiers added to the URLs of websites when visitors come to those pages.
This means that if a website is accessed multiple times by different users, they will all have distinct session IDs in the URL associated with their visits.
These session IDs can create duplicate content issues because search engine crawlers won’t realize that the other versions of the same page are exactly the same when it comes to content — all they see is a different URL for each visit.
As a result, each version of a page can be indexed separately, leading to multiple instances of the same content potentially being indexed by Google.
Thin Content
Image source: Twaino
Thin content can also cause duplicate content issues on a website. This typically happens when multiple articles based on one topic are created with very little or no useful information.
Generic eCommerce Product Pages
Generic ecommerce product pages can also cause duplicate content issues. This usually happens when vendors try to list their products on multiple sites without adjusting the page content for each of those sites. As a result, search engine crawlers may index all of these versions separately, leading to multiple pages with the same content appearing in the SERP listing.
Now that you know all the potential causes of duplicate content, let's dive into the question everyone is asking, "Does duplicate content hurt your SEO?"
Does Duplicate Content Hurt Your SEO?
Yes, duplicate content can have a negative impact on your SEO. Google and other search engines may penalize websites that contain duplicate content, as it can be seen as an attempt to manipulate SEO rankings.
This is why it's important to make sure that all of the content on your website is unique and original.
Having duplicate content can lead to a number of issues such as decreased visibility in SERPs, reduced crawl rate from search engine bots, and even potential penalties from search engines.
Duplicate content can also cause confusion for users who are searching for specific information.
To avoid any potential issues with duplicate content, you should take steps to ensure that Google and other search engine crawlers can differentiate between the original content and the duplicate pages.
Duplicate Content Penalty: Fact or Fiction?
Many people have wondered if there is such a thing as a duplicate content penalty, and the answer is no - not in the way that you'd think.
Search engines may punish websites that contain duplicate content, as it can be seen as an attempt to manipulate rankings. However, there's no such thing as a duplicate content penalty specifically.
According to Google, "Duplicate content generally does not result in a site being removed from the Google index or suffering any other penalty. It’s not always immediately obvious when two pieces of content are considered duplicates." In other words, Google will not necessarily penalize websites for having duplicate content.
However, it's important to note that while Google won't necessarily punish sites with duplicate content, they may still take action in certain cases - such as decreasing the visibility of websites with significantly similar content or multiple copies of the same page. This can lead to issues such as reduced crawl rate from search engine bots and confusion for users who are searching for specific information.
How to Avoid Duplicate Content SEO Issues
Now that you know all the causes of duplicate content and its effect on SEO rankings, we're going to share some of the most common ways to fix duplicate content issues.
Rel=Canonical Tag
Canonical tags are HTML elements that help webmasters avoid duplicate content issues by indicating which URL should be used for indexing purposes. By using canonical tags, webmasters can prevent search engines from indexing multiple versions of the same page, which helps them avoid potential penalties for duplicate content.
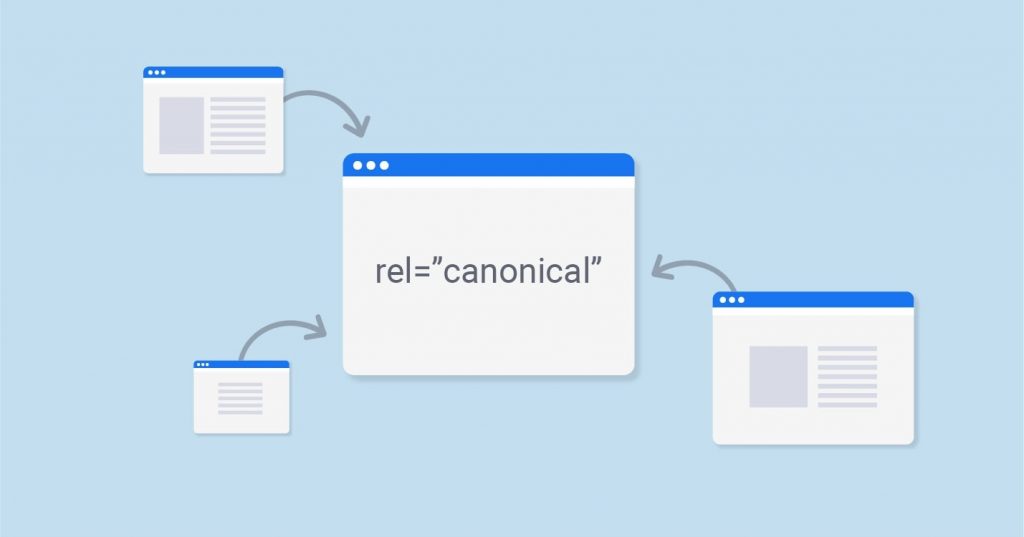
Image source: Digital Garg
Canonical tags can also be used to consolidate link equity and direct crawlers to the desired version of the page.
This is especially helpful in cases when there are several different URLs pointing to the same content, such as with pages that contain session IDs or tracking parameters.
Using canonical tags is an important part of any webmaster's duplicate content strategy as they can help ensure that only one version of a page is indexed and penalization is avoided.
Additionally, they can improve user experience by redirecting users to the most relevant version of a page.
301 Redirects
A 301 redirect is a permanent HTTP status code used to tell web browsers and search engines that a page has been moved permanently to a new address.
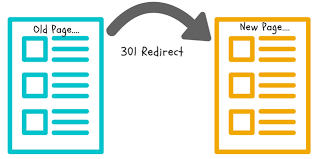
Image source: Infolaw.co.uk
Unlike canonical tags which indicate to search engines which version of the page should be indexed, 301 redirects actually direct bots and users to the new location when they try to access the original page.
Using 301 redirects helps webmasters avoid potential issues with duplicate content by ensuring that any links pointing to an outdated URL are properly redirected. This helps ensure that link equity is not lost and your website does not receive any penalties for having multiple versions of the same page.
Additionally, it can help improve user experience by directing them to the most relevant version of the page.
While both canonical tags and 301 redirects are useful tools for avoiding duplicate content issues, they serve different purposes: Canonical tags indicate which version of a page should be indexed while 301 redirects physically redirect users and crawlers from one URL to another.
It's important to understand the differences between these two tools in order to make sure you are using them correctly.
Consolidate Similar Pages
Consolidating similar pages is an important part of SEO because it helps to avoid duplicate content issues.
Consolidating similar pages into one comprehensive resource ensures that there is only one version of the content available, eliminating any potential confusion or ranking issues.
Additionally, consolidating similar pages can help to create a more user-friendly experience by providing visitors with all the information they need in one place.
This can help improve engagement and keep visitors on your site longer, leading to better overall SEO performance.
Meta Robots Noindex

The meta robots noindex tag can be used to avoid duplicate content issues. This tag tells search engines not to index a page, which can prevent duplicate content from appearing in the SERPs. Unlike canonical tags or 301 redirects, the noindex tag does not create any redirects – it just tells search engines not to index the page.
The noindex tag should be used when you do not want a particular page to appear in the SERPs at all.
For example, it might be used on thin pages with little content, pages with sensitive information, out-of-date versions of a page that have been replaced with something more up-to-date, and pages that are still under construction but have been inadvertently indexed by Google.
When you use the noindex tag, it’s important to make sure you also include a “noarchive” tag as well; this will ensure that even if the page is crawled by search engines, it won’t be cached and stored in their indexes.
Using the meta robots noindex tag is a good way to avoid duplicate content issues without having to delete or redirect existing pages.
If your goal is to consolidate multiple versions of similar content into one definitive version (which has benefits for both users and SEO), then using a canonical tag or 301 redirects may be a more appropriate solution.
Conclusion
In the world of SEO, there's no denying that duplicate content can be a real headache.
But with careful planning and understanding of what causes it – as well as how to prevent it - you'll be able to keep your website in tip-top shape for improved user experience!
Applying these useful tips can help make sure your rankings stay high so everyone will know exactly where they should go when looking up information.